Foot & Ankle
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
The posterior tibial tendon plays a crucial role in providing stability to the foot and maintaining the arch during walking. This tendon runs from the calf muscle to the bones in the mid-foot, supporting the arch of the foot. When this tendon becomes inflamed, torn, or dysfunctional, it leads to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD), a common cause of foot and ankle pain and flatfoot.
Symptoms of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Symptoms of PTTD typically develop gradually and may worsen over time, particularly with continued activity. Common symptoms include:
- Pain on the inside of the foot and ankle, often accompanied by swelling.
- Pain with activity: High-impact or high-intensity activities, such as running or jumping, may exacerbate the pain.
- Pain on the outside of the ankle: As the tendon fails, the foot may collapse, causing the heel bone to shift outward, placing pressure on the outside of the ankle.
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods due to pain or weakness in the foot and ankle.
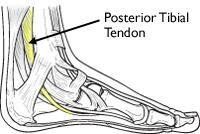
Causes of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
PTTD can result from several causes:
- Acute injury: A fall or trauma can tear or inflame the posterior tibial tendon.
- Overuse: High-impact sports or repetitive stress on the tendon can lead to inflammation and eventually cause damage.
- Additional risk factors: Conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and hypertension can increase the risk of developing posterior tibial tendon dysfunction by putting additional strain on the tendon.
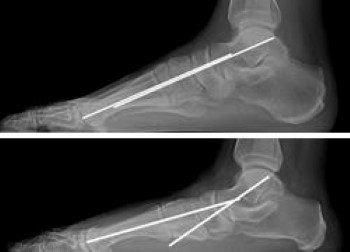
Diagnosis of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Diagnosis of PTTD begins with a medical consultation, where the healthcare provider will assess the patient's medical history and physical condition. The exam will include testing for pain, changes in ankle position, flexibility, strength, and range of motion. Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound may be ordered to visualise the tendon, confirm the diagnosis, and rule out other potential abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
Non-Operative Treatment
In the early stages, PTTD can often be managed conservatively through non-surgical treatment options:
- Rest and reducing activity to prevent further strain on the tendon.
- Ice application: Regular ice packs can help reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain and inflammation.
- Steroid injections: For cases of persistent inflammation, a corticosteroid injection may be used to provide relief.
- Immobilisation: The use of a cast or walking boot can protect the tendon and limit movement to allow it to heal.
- Orthotics: Custom insoles or braces designed to support the arch of the foot can help reduce stress on the tendon and improve foot function.
- Physical therapy: Exercises aimed at strengthening the posterior tibial tendon and improving flexibility can help restore function and reduce pain.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if the tendon is severely damaged, surgery may be required. Surgical options include:
- Tenosynovectomy: A procedure in which the inflamed tendon tissue is removed to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Tendon transfer: In cases where the tendon is severely damaged, a tendon from another part of the foot may be used to replace the damaged posterior tibial tendon.
- Arthrodesis: For patients with significant arthritis, arthrodesis involves realigning and fusing the bones of the foot to form a single solid bone, eliminating pain and improving stability.
- Osteotomy: This procedure involves cutting and repositioning the bones of the heel and midfoot to create a new arch for the foot.
Why Choose Dr. Ryan du Sart for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Treatment?
Dr. Ryan du Sart is a highly skilled orthopaedic surgeon with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating foot and ankle conditions, including posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. With a personalised and patient-centred approach, Dr. du Sart offers comprehensive care, from conservative management to advanced surgical interventions, tailored to meet each patient's specific needs and goals.
Book a Consultation
If you are experiencing foot or ankle pain, particularly on the inside of the ankle, or if you suspect posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing further damage. Book a consultation with Dr. Ryan du Sart today to discuss your treatment options and begin your path to recovery.
Phone: (08) 9779 9767
Email: admin@ryandusart.com.au
Locations:
6 Higgins Street, South Bunbury, WA 6230
20 Prince Street, Busselton, WA 6280
References:
- Kaufman, K. R., & Greenfield, S. (2018). "The Role of the Posterior Tibial Tendon in Foot Function: A Review." Journal of Foot and Ankle Research, 11(1), 29-35.
- Hansen, J. M., & Dobson, J. M. (2020). "Surgical Techniques for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction: A Review of Methods and Outcomes." Foot and Ankle Clinics, 25(3), 365-375.
- Gould, M. T., & Miller, T. L. (2019). "Management of Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction in Adults: A Clinical Perspective." Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 14(1), 59-65.

