Foot & Ankle
Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) into the ankle joint to diagnose and treat various ankle conditions. This technique has become increasingly popular due to its numerous advantages, including smaller incisions, reduced scarring, faster healing, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
What is Ankle Arthroscopy?
Ankle arthroscopy is an advanced form of keyhole surgery that allows surgeons to examine the inside of the ankle joint. This procedure is used to address a variety of ankle disorders, such as:
- Excessive scarring or synovial proliferation in the ankle joint after an injury, which is a common cause of ankle pain.
- Debridement or removal of injured cartilage, such as osteochondral lesions.
- Loose bodies that may be causing pain or restricting movement in the joint.
- Shaving intra-articular osteophytes (bone spurs) that can cause discomfort and limit range of motion.
- Adjunct to other procedures such as ankle ligament reconstruction or ankle fusion surgery (arthrodesis).
- An adjunct to other procedures such as
- Ankle Ligament Reconstruction.
- Ankle Fusion Surgery (Arthrodesis).
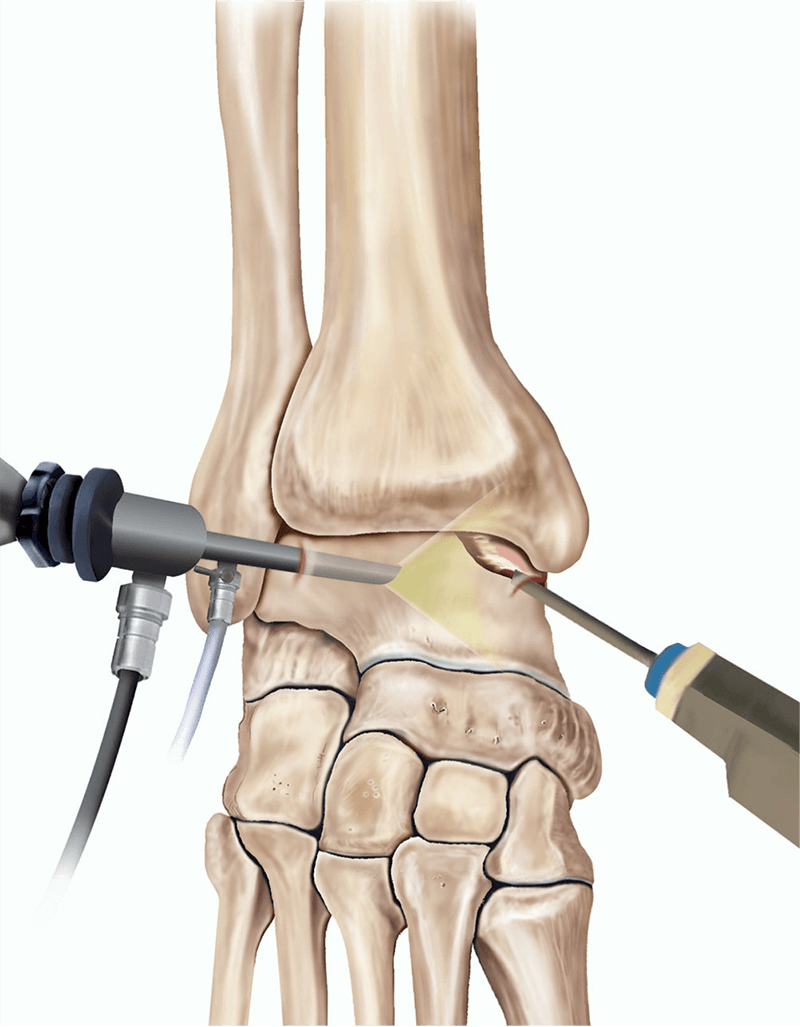
Procedure for Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy is typically performed through two to three small incisions around the ankle. A small telescope with a camera at the end is inserted into the joint, and images are projected onto a monitor, allowing the surgeon to closely examine the ankle. The surgeon looks for cartilage damage, inflamed synovial tissue (synovitis), scarring, or bone spurs. If treatment is needed, specialized instruments are used through additional small incisions to address the issue. After the procedure, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are stitched closed, covered with dressings, and bandaged.
Benefits of Ankle Arthroscopy
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions and reduced scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
- Quicker Recovery: Faster recovery times, allowing patients to return to normal activities more quickly.
- Reduced Pain: Less postoperative pain, especially compared to open surgeries.
- Preservation of Joint Function: It effectively treats various conditions while preserving joint function and mobility.
After Your Operation: Recovery and Pain Management
Post-surgery, you will be instructed to elevate your foot to reduce swelling. Local anaesthetic will be administered to provide pain relief, temporarily numbing the foot and toes. During your hospital stay, you will be given regular pain relief medications, typically consisting of paracetamol and anti-inflammatory drugs. Stronger painkillers may be prescribed in the early stages but are gradually phased out as you heal.
Mobility After Ankle Arthroscopy
Following the procedure, your ankle will be immobilised in a splint or cast, and the duration of immobilisation will depend on the severity of the injury and the extent of the repair performed. For the first two weeks, it’s recommended to keep the foot elevated to promote healing and minimise swelling. You may begin to mobilise as tolerated after surgery, but the timeline for full mobility varies depending on the nature of the surgery. Physiotherapy may be required to ensure optimal recovery and strengthen the ankle. Dr. du Sart will provide specific guidance on your rehabilitation plan and timeframes based on your individual case.
Return to Work and Sport
Return to work depends on the nature of your occupation and the extent of your surgery. Generally, two weeks off work are recommended to allow the wound to heal and reduce swelling. If your job involves standing or walking for extended periods, you may need 4 to 6 weeks before returning to full duties. For more physically demanding jobs, such as those requiring heavy lifting or running, it may take 6 to 9 weeks to resume work.
In terms of sports, light activities such as jogging may be resumed 6 to 9 weeks post-surgery, depending on the type and level of activity. Full recovery is typically expected within 3 months.
Driving After Ankle Arthroscopy
The timing of your return to driving will vary depending on the surgery and whether your left or right ankle was operated on. If your left ankle was operated on and you drive an automatic car, you may be able to return to driving sooner, usually within two weeks. However, if your right ankle was operated on, it may take longer—typically 12 weeks or more—before you are cleared to drive. Dr. du Sart will provide personalised advice during your post-operation review.
Why Choose Dr. Ryan du Sart for Ankle Arthroscopy?
Dr. Ryan du Sart is a highly skilled orthopaedic surgeon with extensive experience in performing ankle arthroscopy. His approach is patient-centered, ensuring the most effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Dr. du Sart uses advanced minimally invasive techniques to achieve the best possible outcomes and ensure a fast recovery.
Book a Consultation
If you're suffering from ankle pain or discomfort due to conditions such as osteochondral lesions, synovitis, or bone spurs, consider booking a consultation with Dr. Ryan du Sart. With early intervention, ankle arthroscopy can significantly improve your quality of life and help you return to your normal activities.
Phone: (08) 9779 9767
Email: admin@ryandusart.com.au
Locations:
6 Higgins Street, South Bunbury, WA 6230
20 Prince Street, Busselton, WA 6280
References:
- Guillo, S., & Bonnevialle, N. (2016). "Ankle Arthroscopy: Techniques and Indications." Orthopaedic Clinics of North America, 47(4), 667-678.
- Wright, C. (2019). "Minimally Invasive Ankle Arthroscopy: Advances and Outcomes." Foot & Ankle Clinics, 24(3), 377-390.
- Bollier, M., & Do, H. (2020). "Outcomes of Ankle Arthroscopy for Chronic Ankle Pain and Instability." Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 59(1), 54-60.

