Foot & Ankle
Ankle Fractures: Expert Diagnosis and Treatment in Bunbury & Busselton
An ankle fracture, commonly referred to as a broken ankle, involves a break in one or more of the bones in the ankle joint. This injury can result from various causes, including sports activities, falls, or accidents. Symptoms often include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot.
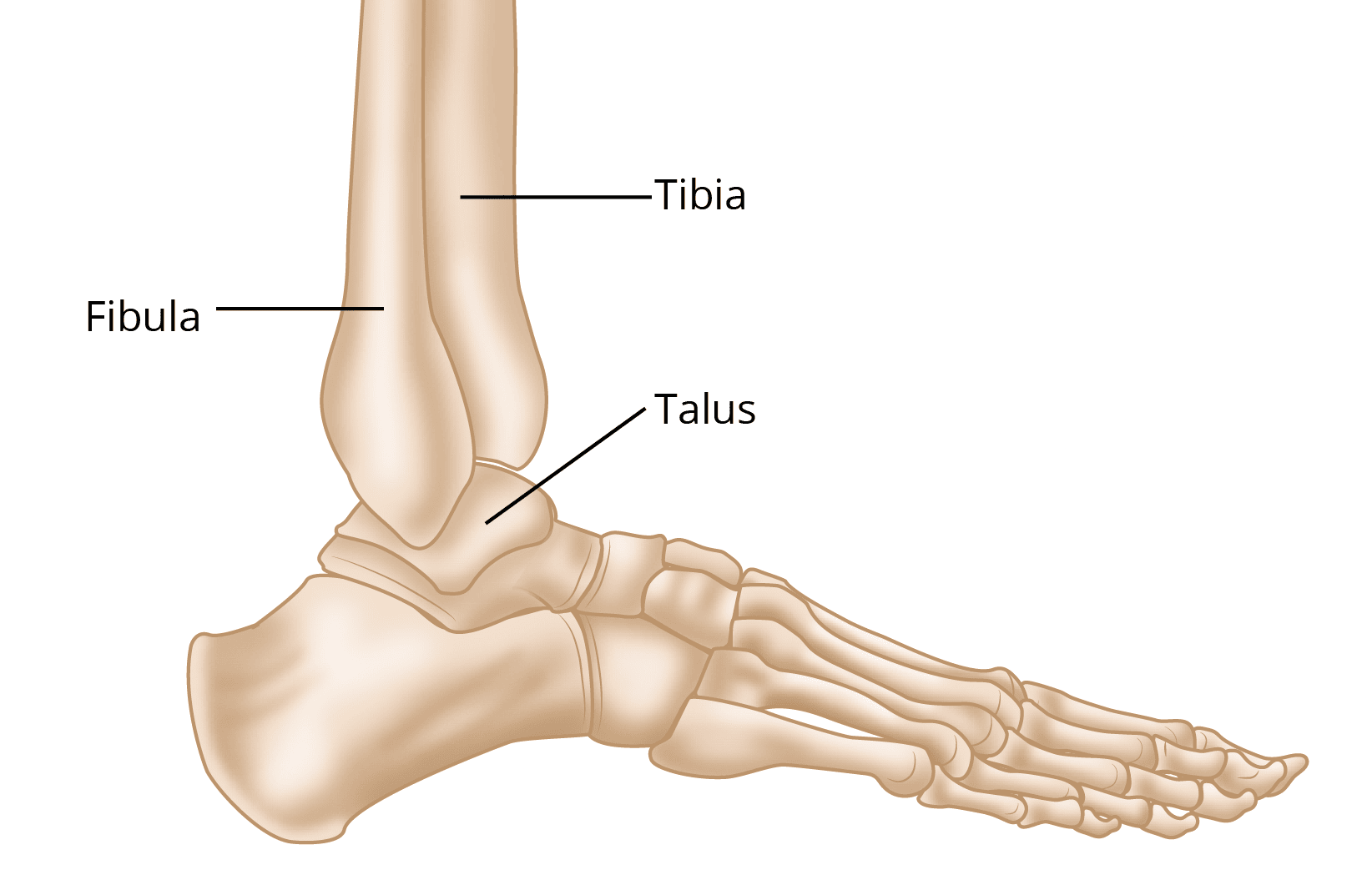
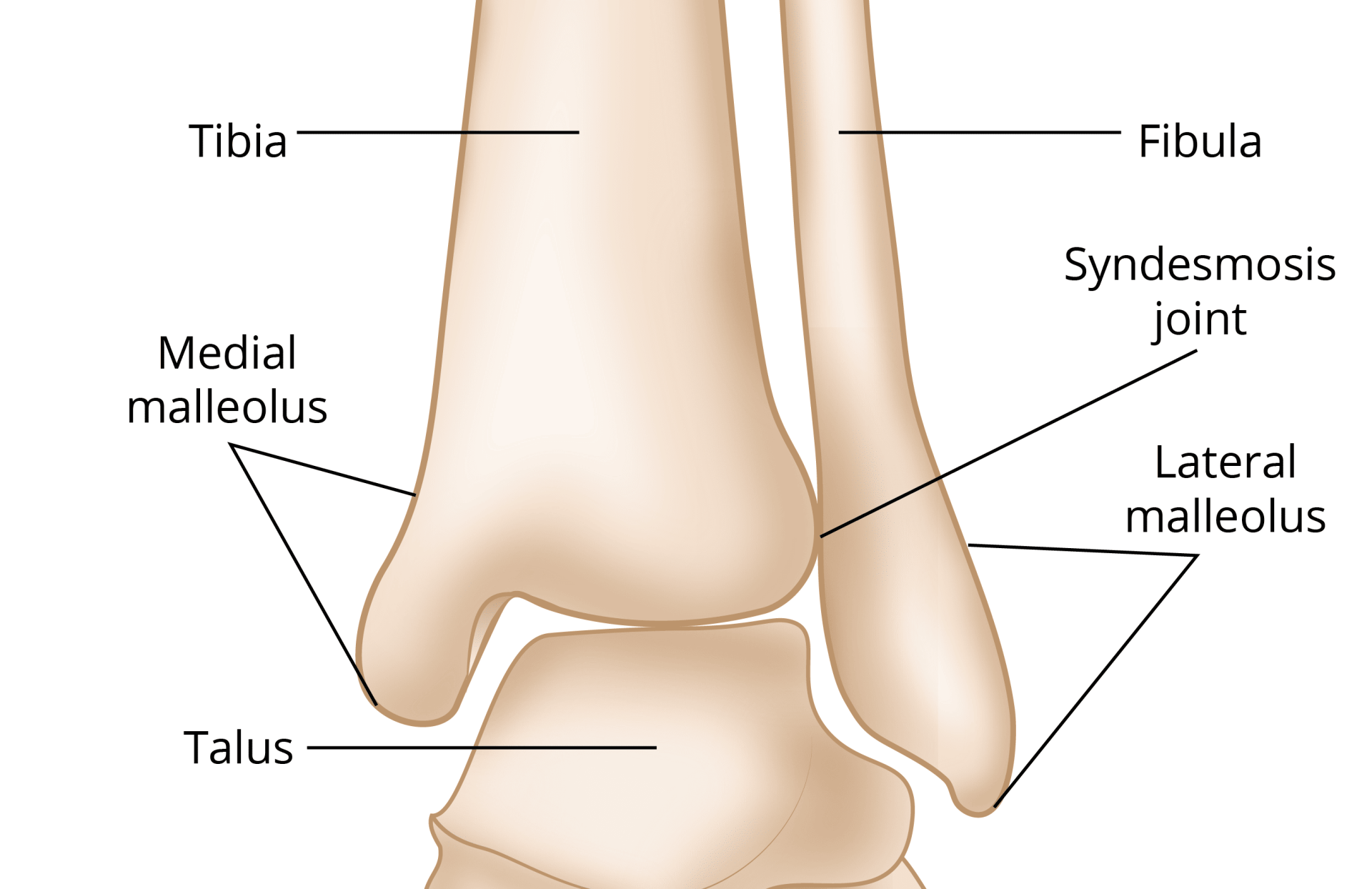
Understanding Ankle Fractures
An ankle fracture (also commonly referred to as a broken ankle) occurs when one or more of the bones in the ankle joint break due to trauma. The ankle joint is composed of three primary bones: the tibia (shin bone), fibula (smaller bone on the outside of the ankle), and talus (the bone that connects the leg to the foot). An ankle fracture can range from a simple break in one bone to a complex injury that involves multiple bones and ligaments. It is a serious injury that can affect mobility and require timely treatment.
Ankle fractures are common, particularly in individuals who engage in sports or high-impact activities. In Australia, approximately 1 in 10 fractures seen in emergency departments are ankle fractures, with high rates observed in both younger athletes and older adults due to falls.
Types of Ankle Fractures
Ankle fractures can vary in severity and involve different bones in the ankle. The most common types of ankle fractures include:
- Lateral Malleolus Fracture: A break in the fibula (the smaller bone on the outside of the ankle). This is the most common type of ankle fracture and is often caused by an inversion injury (twisting of the ankle).
- Medial Malleolus Fracture: A fracture of the tibia (the larger bone on the inside of the ankle), which can occur with or without damage to the ligaments supporting the ankle.
- Bimalleolar Fracture: This type involves fractures in both the medial and lateral malleoli, often resulting in instability and requiring surgical intervention.
- Trimalleolar Fracture: Involves fractures of the medial, lateral, and posterior malleoli. This type of fracture is more complex and typically requires surgery to restore function and stability.
Accurate diagnosis of the specific type of fracture is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment and to prevent complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Ankle fractures can result from various causes, most commonly trauma or injury. Key causes and risk factors include:
- Sports Injuries: High-impact sports such as soccer, rugby, basketball, and running put excessive strain on the ankle joint and are common causes of ankle fractures.
- Falls: Older adults are particularly vulnerable to ankle fractures due to weakened bones and reduced balance. A fall from standing height or slipping on wet surfaces is a common cause of injury.
- Trauma or Accidents: Injuries sustained from motor vehicle accidents, accidents at home, or workplace injuries can cause severe ankle fractures.
- Previous Ankle Injury: A history of ankle sprains or fractures increases the likelihood of future injuries, especially if the joint is unstable or the ligaments are weakened.
- Osteoporosis: Reduced bone density due to osteoporosis or other bone-related conditions increases the risk of fractures, even with minor trauma.
Symptoms of an Ankle Fracture
Recognising the symptoms of an ankle fracture is essential for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Severe pain: Intense pain in the ankle, particularly when attempting to bear weight.
- Swelling and bruising: Swelling around the ankle joint is common, with bruising often visible immediately or in the days following the injury.
- Inability to bear weight: Difficulty walking or standing on the affected foot due to pain and instability.
- Visible deformity: In severe cases, a visible misalignment or deformity of the ankle joint may occur.
- Tenderness and restricted range of motion: Pain when touching the injured area or trying to move the ankle, especially in cases of more severe fractures.
If you experience any of these symptoms following an injury, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis
Dr. Ryan du Sart will perform a thorough clinical assessment to diagnose the severity and type of ankle fracture. This includes evaluating the location of pain, swelling, and deformity, as well as assessing range of motion in the ankle. Imaging tests, such as X-rays and sometimes CT scans or MRIs, are necessary to confirm the diagnosis and understand the extent of the fracture.
- X-rays: The most common imaging tool used to detect ankle fractures and determine the type and location of the break.
- CT Scans and MRIs: For complex fractures or if soft tissue damage (such as ligament tears or cartilage damage) is suspected, additional imaging may be required to evaluate the injury in more detail.
Early and accurate diagnosis allows for the development of the most appropriate treatment plan, helping to ensure the best possible recovery.
Treatment Options for Ankle Fractures
Dr. Ryan du Sart offers both non-surgical and surgical options for treating
ankle fractures, tailored to the severity and type of fracture.
Non-Surgical Management
For stable fractures or non-displaced fractures, non-surgical treatment may be sufficient. Non-surgical treatment options include:
- Immobilisation: The foot and ankle may be placed in a cast or walking boot to restrict movement and allow the bones to heal properly.
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE): This well-known method is used to reduce swelling and manage pain. Applying ice to the injured area and elevating the foot will help prevent further swelling.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, are commonly recommended for managing pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: After the bone has healed, physical therapy is essential to regain strength, flexibility, and full function in the ankle joint.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical intervention may be necessary for displaced fractures, bimalleolar fractures, or trimalleolar fractures, where the bones have shifted out of alignment. Common surgical treatment options include:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): This procedure involves surgically realigning the bones and securing them with metal plates, screws, or rods to ensure proper healing and restore stability to the ankle.
- External Fixation: In more complex cases, an external frame may be used to stabilise the bones during healing. This approach is often used when there is significant soft tissue injury alongside the fracture.
- Arthrodesis: In severe cases of ankle joint instability, a fusion of the joint may be performed to restore stability and reduce pain.
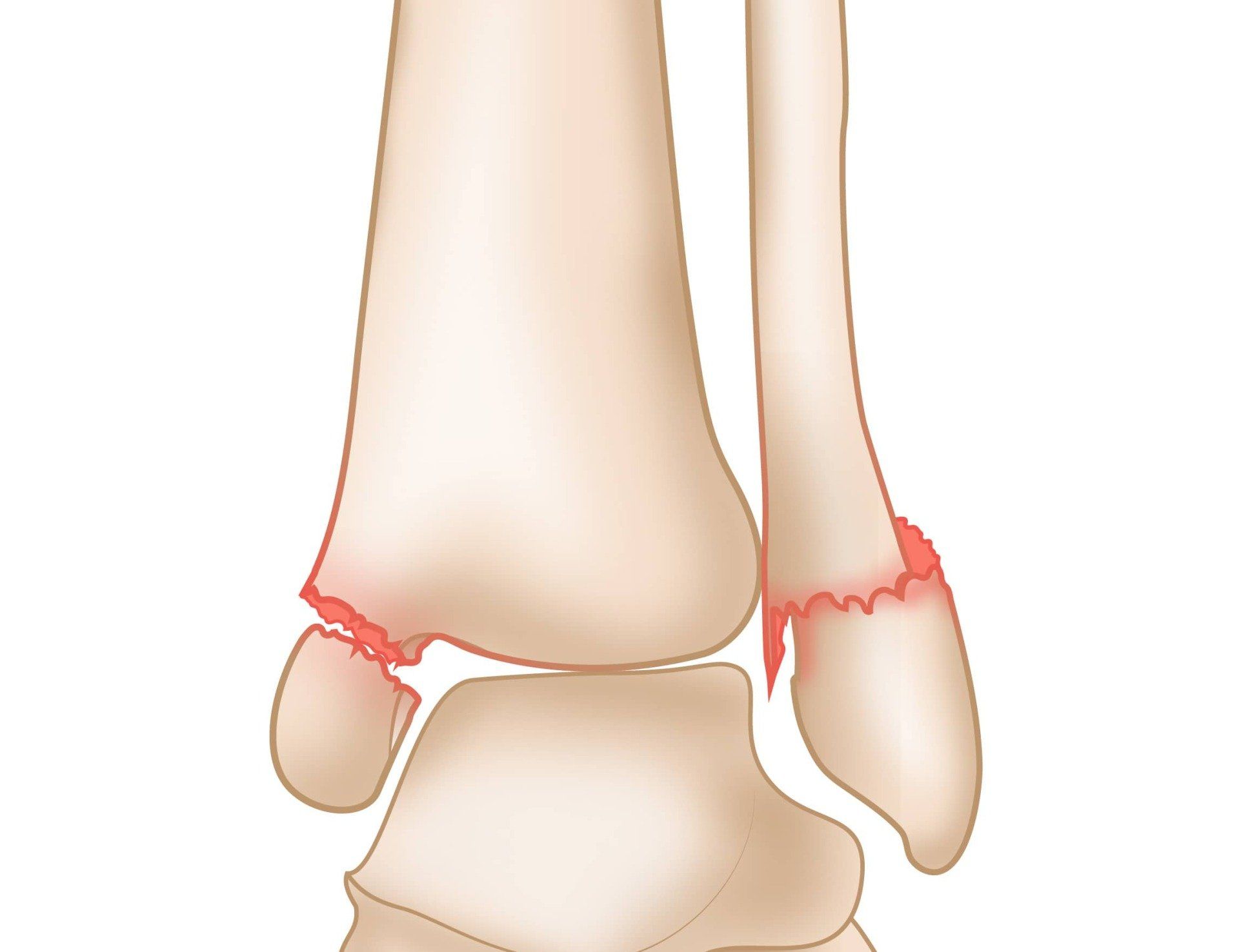
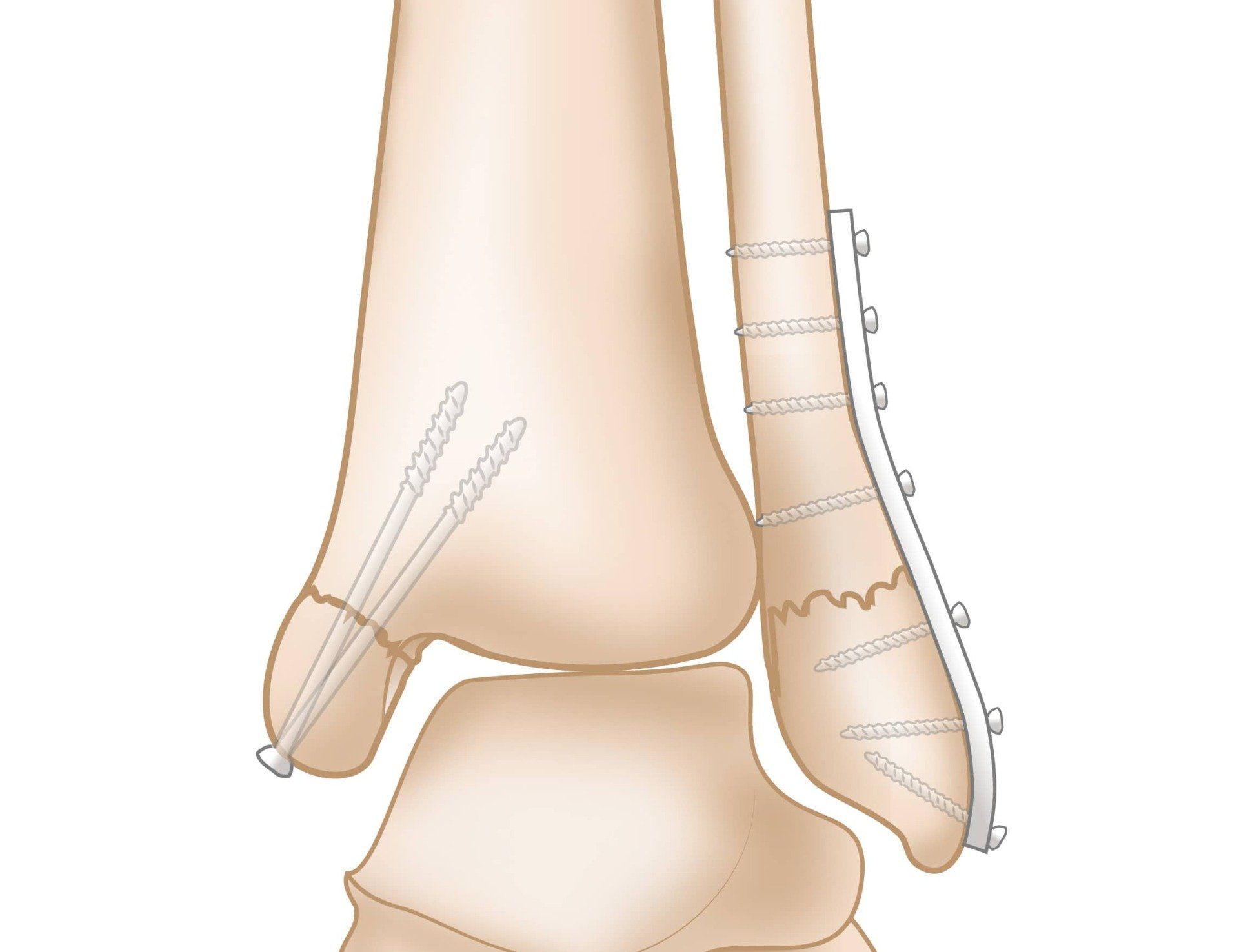
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery time for an ankle fracture varies depending on the severity of the fracture and the chosen treatment method. However, a typical recovery process includes:
- Initial Immobilisation: After surgery or non-surgical treatment, the foot will be immobilised in a cast or boot for 6–8 weeks to allow the bones to heal properly.
- Weight-Bearing and Physical Therapy: As the bones heal, patients will gradually begin bearing weight on the affected foot. Physical therapy will help restore strength, mobility, and flexibility in the ankle joint.
- Return to Activities: Once the ankle has fully healed and strength is restored, patients can gradually return to normal activities. Athletes and individuals involved in high-impact sports may require additional time for full recovery.
The full recovery period may range from 3–6 months, with athletes potentially needing up to 9–12 months to return to high-performance levels.
Why Choose Dr. Ryan du Sart?
Dr. Ryan du Sart is a highly skilled orthopaedic surgeon with extensive experience in the treatment of foot and ankle fractures. He offers state-of-the-art care and tailored treatment plans to ensure the best possible outcomes for his patients. Dr. du Sart uses advanced surgical techniques and rehabilitation protocols to ensure that patients receive the most effective and efficient care.
Schedule a Consultation
If you suspect you have sustained an ankle fracture or are experiencing symptoms related to an ankle injury, it’s essential to seek prompt medical attention. Dr. Ryan du Sart offers expert diagnosis and treatment options to ensure you receive the best possible care and a smooth recovery process.
Phone: (08) 9779 9767
Email: admin@ryandusart.com.au
Locations:
6 Higgins Street, South Bunbury, WA 6230
20 Prince Street, Busselton, WA 6280
References:
- Cleveland Clinic. (2020). Ankle fractures.https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15298-ankle-fracture
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Ankle fracture.https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ankle-fracture/
- Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma. (2019). Surgical outcomes of ankle fractures.https://journals.lww.com/jorthotrauma
- Royal Australian College of Surgeons (RACS). (2020). Management of ankle fractures.https://www.surgeons.org

